
In the current competitive market for automotive, Customer relationships are the key to success more than ever. Automotive dealers aren’t simply selling cars. They’re also managing expectations, experiences, and the long-term loyalty of customers. This is the point at which the Customer Relations Management (CRM) tools are an industry-changing technology. Modern CRM systems streamline sales, boost customer retention, improve communication, and assist dealerships in making better decisions based on data.
We’ll discuss what a is CRM System and how it is for modern car dealerships, the ways they can improve efficiency in operations, and what essential benefits they can bring to the dealership’s ecosystem.
In today’s technologically-driven business world, maintaining strong relationships with your customers is no longer a luxury but an essential. This is why an efficient customer Relationship Management (CRM) program is required for every business, regardless of size.
What is CRM System?
The CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system aids businesses in monitoring, analyzing, and enhancing their interactions with current and potential customers. According to a leading vendor:
CRM is a shorthand term for the management of customer relationships. It’s a system that helps control the company’s interactions with current and future customers. ” – Salesforce
A different service provider expands this definition to include the entire lifecycle.
“Customer relations management (CRM) is a set of interconnected technologies that is used to monitor, record, and control the interactions of a business with its current and potential customers.” – IBM
More precisely, CRM systems collect information about customers (contact histories, transactions, and even contacts) and store it centrally, and permit coordinated interactions between the sales, marketing, and customer support.
Why is a CRM System important?
In a time when customers want fast, personalized interactions, businesses that do not have a CRM system typically face unorganized data, delayed follow-ups, and missed opportunities. The reasons why CRMs are essential:
- Unified View of the Client: The majority of businesses employ dozens or even hundreds of apps; however, customers expect consistency. A CRM consolidates data so that everyone who interacts with customers sees the same information.
- Efficiency and Cost Control: By automating a lot of manual procedures (lead capture and follow-up, as well as scheduling services), CRMs can reduce the amount of time and errors.
- Data-Driven Choices: With analytics integrated into the system, companies can monitor sales pipelines, predict demand, and understand the behaviour of their customers.
- Improved Customer Experience, Retention, and Satisfaction: The moment that teams have access to the full interactions, they can react more effectively and build loyalty.
How does a CRM System Works?
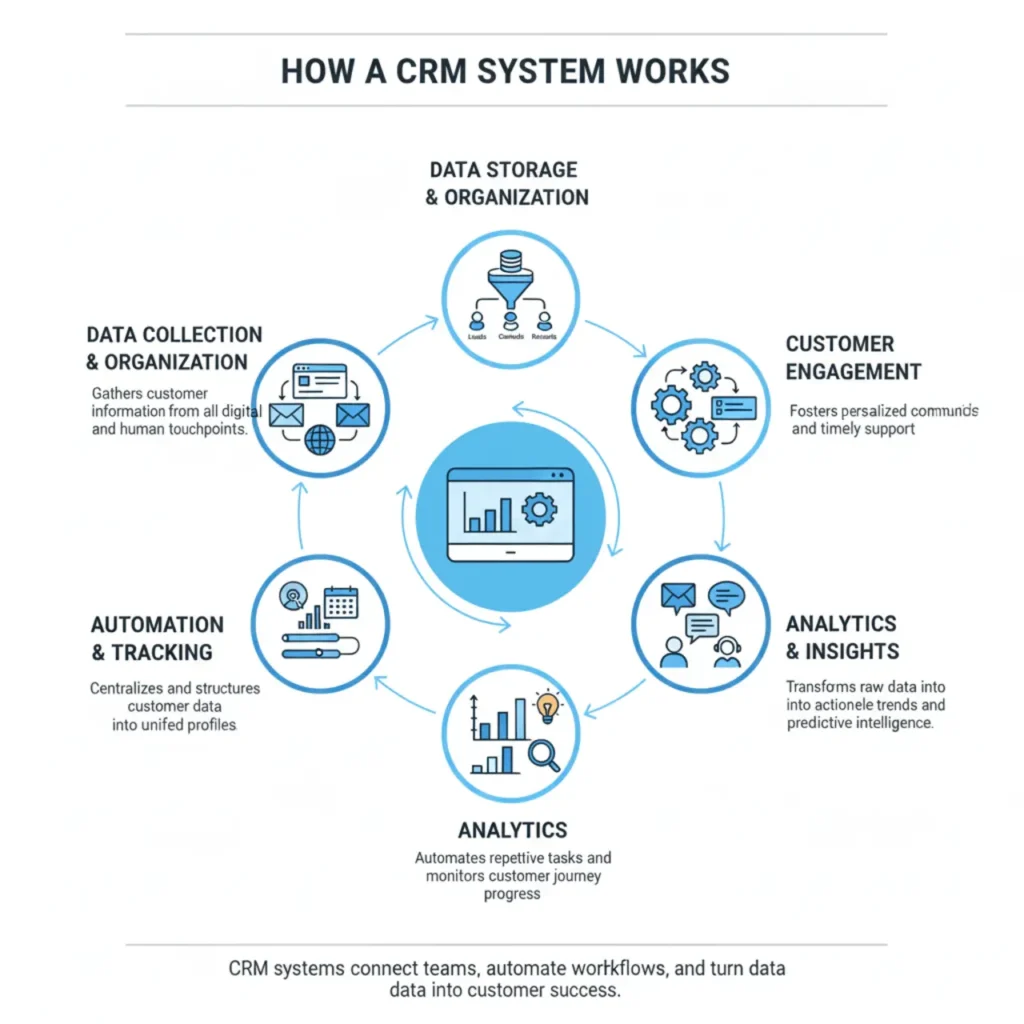
A CRM system typically performs fundamental functions throughout the life cycle of a customer. They include:
- Contact Management and Lead Management: Lead and contact management: Capturing leads from various channels (web, social, referrals) and storing contact information, as well as the assignment of leads to reps for sales.
- Pipeline Management and Managing Opportunities: Monitoring prospects stage deals, monitoring closing rates, forecasting revenue.
- Marketing Automation: Running campaigns, segmenting customers, sending targeted messages, measuring engagement.
- Customer Service and Support: Tracking customer service and support cases, recording resolutions, and keeping track of service history to ensure that support teams are aware of the latest information.
- Analytics and Reporting: Dashboards that show the performance of metrics, customer behavior patterns, and ROI of campaigns.
- Automating Workflow and Integration: Integration of CRM to other systems (ERP, marketing, finance, etc.) and automating tasks such as reminders, follow-ups, and so on.
Different types of CRM Systems
It is essential to realize that CRM systems aren’t all the same. They differ by the function, the deployment method, and the business focus. As per IBM:
- Operational CRM: It focuses on front-office operations – sales automation, marketing automation.
- Analytical CRM focuses on analyzing customer data to gain insights, as well as forecasting and identifying trends.
- Collaborative CRM: Also known as strategic CRM, this approach aims at breaking the silos that separate teams so that several teams collaborate and share information about customers.
A different axis of classification:
- Cloud-based vs. On-premise: Cloud CRMs can be accessed via the internet and are easy to set up and expand. On-premise systems are set up on local servers and require additional infrastructure.
- All-in-One or Industry Specific: CRMs Certain CRMs are designed to cater to specific industries (e.g., healthcare or financial services, etc.), and others are broad-based and highly customizable.
Example: A brand selling retail can track the journey of a client, starting with their first visit until their final purchase, providing personalized services and faster customer assistance.
Key Features of a Modern CRM
When it comes to evaluating or describing the current CRM systems, the following features stand out:
- A single database for customers: One record of every customer, including the contact information, purchases, history of purchase, and interaction across all channels.
- Multi-Channel Interaction Monitoring: Email messages, telephone calls, social media, live chat, all recorded and available.
- Automating Workflows: For instance, if an opportunity is created, the system will automatically assign tasks, emails to follow up, and schedule test drives and demonstrations.
- Dashboards and Analytics: Visual tools to show the speed of pipelines and churn of customers, as well as the effectiveness of campaigns.
- Capabilities for Integration: Connects to other business systems (e.g., accounting, inventory, ERP) to facilitate smoother operations.
- Accessibility and Mobility: Mobility and accessibility: Many CRMs permit users to access data via mobile devices, which can be used to support remote work or field sales.
- Scalability and Customization: Ability to expand with the company and adapt to specific industries or workflows.
- Data Governance and Security: Security and data governance: Security of customer data is vital. Modern CRMs require strong security and compliance tools.
Benefits of Implementing a CRM
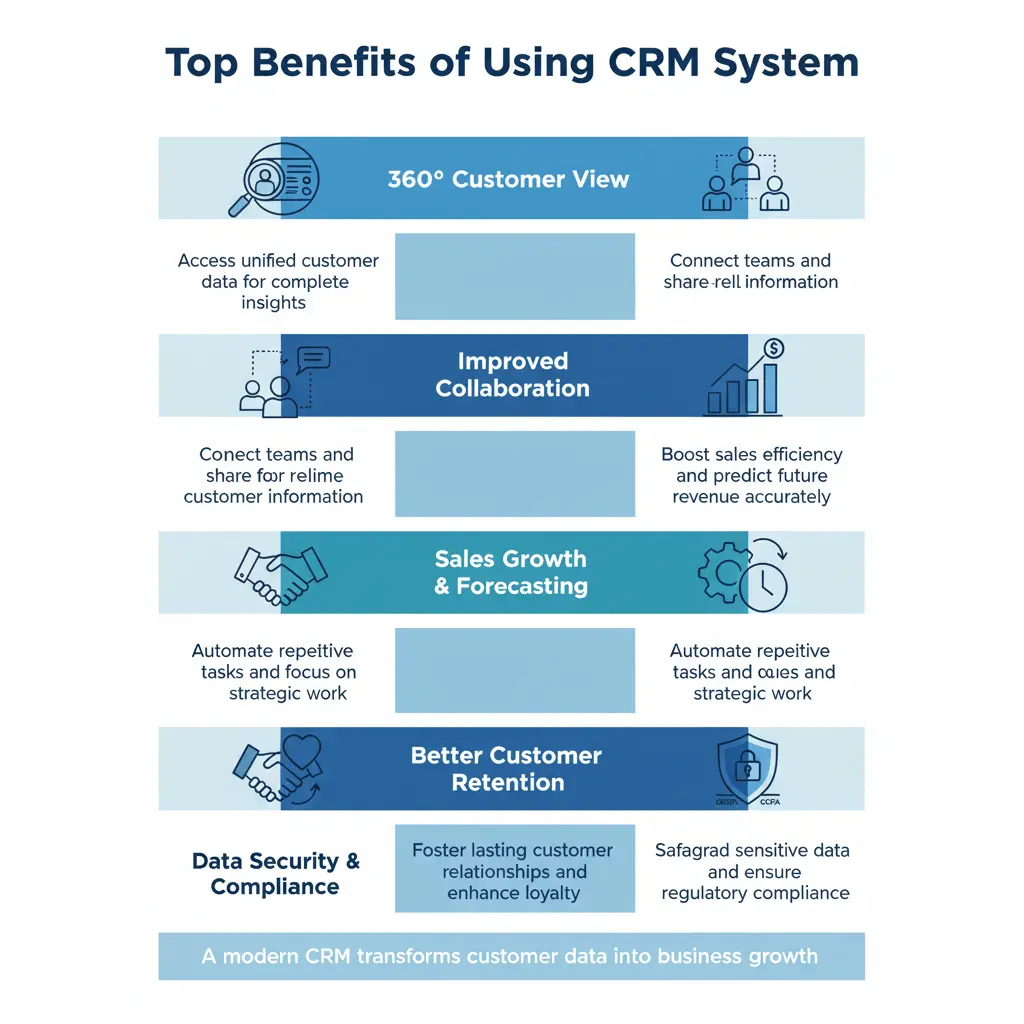
When implemented correctly, the CRM will provide tangible benefits to businesses:
- Improved Sales Efficiency and Revenue: A better understanding of pipelines means better conversion rates. For instance, one vendor has reported a 30% increase in sales revenue and quicker closing metrics for deals.
- Increased Retention of Customers and Value Lifetime: By being in contact with customers and proactively responding, organizations can reduce the rate of churn.
- Reduced Costs and Improved Operational Effectiveness: Reduced manual work, fewer mistakes, and better coordination of teams.
- Enhances user satisfaction: The moment that teams are in full view, it makes customers feel more understood, and the service can be more personalized.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Organizations can analyze patterns, spot opportunities, and optimize their strategies.
- Scalability and Agility: Cloud-based CRMs enable businesses to adapt and scale their operations rapidly as needed.
Why Businesses Need a CRM System Now?
In today’s world of the customer-centric economy, companies aren’t able to compete solely with regard to price or products but rather on the experiences. Customers expect instant responses, highly personalized communications, and seamless interaction at every point of contact, including social media and chat support.
To meet these requirements in a consistent manner is almost impossible without a unified system. That’s why software called CRM (Customer Relationship Management Systems) can play an essential role.
1. 360-Degree View of Customers Across all Departments
A CRM combines information about customers from marketing, sales, and service teams onto one central platform.
The “single basis of fact” guarantees that every department is able to access the same data, from a customer’s purchase history to their most recent ticket for support.
For instance, sales reps can immediately see the latest product that a customer bought and the campaign they were involved with, as well as their open service requests prior to launching an initial phone call. This type of context enables relevant, personal conversations instead of generic outreach.
Data Insight: According to Salesforce users, companies using CRM see an average increase of 29% in sales and an increase of 34% in customer satisfaction because of greater data transparency and better collaboration.
2. Automatization of Repetitive Processes
Contemporary CRM applications automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as the entry of data, reminders to follow up, and lead assignment.
Automation decreases the chance of human error and lets teams focus on more valuable tasks, such as nurturing leads and building relationships.
For example, if someone is a prospective customer who fills in the form on your website, the CRM will then:
- Create a new contact entry,
- The lead should be assigned to the sales representative who is responsible and
- Trigger a personalized email sequence.
This level of automation guarantees that every lead is missed while keeping a professional, consistent approach to the scale.
3. Predictive Insights using AI and Analytics
The most sophisticated CRM systems today incorporate AI-driven analytics, which provide prescriptive insights. The systems are able to analyze vast amounts of customer information to predict behavior, pinpoint vulnerable clients, and suggest the following steps to take.
For example:
- A CRM powered by AI can identify leads that are best suited to conversion, based on previous interactions.
- In retail stores, it is able to predict the customers most likely to abandon their purchase and then trigger a loyalty program to keep customers.
This ability to predict the future allows proactive business decisions and not just reactive ones that ensure the long-term satisfaction of customers and profit.
4. Omnichannel Integration to Provide Seamless Experiences
Today’s consumers interact with brands through many channels, including websites, chat, social media, and via email and phone. They expect their interactions to be unified and consistent regardless of the medium.
A CRM program that combines all of these touchpoints, allowing teams to have a unifying customer history of communications.
For example, if a customer makes an inquiry via live chat and then calls support, the agent has the complete chat transcript and the context, thus avoiding repeated explanations.
This level of omnichannel accessibility ensures that brands have continuity, improve efficiency, and establish greater confidence with their customers.
5. Closing the Gap: Moving from Spreadsheets to Strategies
Despite the numerous advantages, a lot of businesses, particularly smaller and mid-sized ones, still rely on spreadsheets, separate emails, and obsolete software that tracks the interactions of customers.
Although these programs might perform for a brief period, they can result in data fragmentation as well as inconsistent communication and missing opportunities.
A CRM program removes this fragmentation
- Consolidating customer records,
- streamlining team collaboration and
- Giving you actionable insight in real-time.
In another way, CRM bridges the data as well as strategy and is changing the way organizations handle relationships as well as make choices.
The main takeaway from CRM is that it’s not only about managing customers but also about managing all aspects of their experience.
Use Cases for CRM in Various Industries
Although every company benefits from CRM, the impact is dependent on the business. Here’s how different industries leverage CRM systems to increase the growth of their businesses and increase efficiency:
1. Retail & E-Commerce
Online stores and retailers make use of CRM to analyze buying patterns and to tailor marketing.
- Track the history of purchases and carts that have been abandoned.
- Segment customers according to their preferences as well as loyalty status.
- Send customized offers or product recommendations.
- Control loyalty and engagement after purchase.
Examples: A fashion retailer could send specific style suggestions to customers who have returned or provide exclusive early access to the latest collections to VIP customers.
2. Automotive
In the auto industry, CRM helps streamline the service and sales processes.
- Leads can be captured from dealer websites as well as advertisements on social media.
- Test drives can be scheduled, and email automated reminders can be sent.
- Manage follow-ups after sales, such as maintenance reminders and renewals of warranties.
- Track the long-term life cycle of customers beginning with the purchase of the first item through upgrades.
Example: A car dealership could use CRM to inform customers when their car is due for maintenance to increase retention and confidence.
3. Healthcare
For healthcare institutions, CRM helps improve patient relationship management as well as operational efficiency.
- Control patients’ profiles, appointments, and provide feedback.
- Automated reminders for appointments as well as prescriptions.
- Use satisfaction measures to improve care quality.
- Ensure secure, compliant data management (HIPAA/GDPR-ready systems).
Examples: A hospital utilizes CRM to coordinate follow-ups for patients and to automate post-discharge wellness surveys to increase satisfaction and lower readmission rates.
4. Real Estate
Real estate agents rely on CRM to monitor and convert leads through the entire buying journey.
- Manage listings for properties and match client preferences to listings.
- Plan website visits, and then send follow-up emails.
- Track negotiations documents, contracts, and negotiations.
Examples: A realtor is able to follow up with customers following the viewing of a property, offering specific suggestions based on the client’s needs and budget.
5. Education
In the realm of education, CRM systems are utilized to manage the complete student lifecycle, all the way from intake to involvement.
- Handle applications and inquiries.
- Monitor interaction between students and admissions staff.
- Automate reminders for application deadlines.
- Maintain ongoing engagement with alums for fundraising or referrals.
An example: A university makes use of CRM to help nurture potential students via automated email workflows, monitor the rate of conversion, and keep in contact following graduation for events as well as donations.
6. Additional Emerging Use Cases
- Hospitality: Control guest profiles, preferences, and feedback for more personalized stays.
- Financial Services: Automating the processing of loans, tracking compliance, and providing customer service.
- IT and SaaS: Track subscriptions, renewals, and health scores of customers to cut down on the number of customers who churn.
Best CRM Software to Consider (2025)
| CRM Software | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Salesforce Sales Cloud | Large enterprises | AI insights, deep customization, scalability |
| Zoho CRM | Small & medium businesses | Affordable, multichannel, easy automation |
| HubSpot CRM | Startups & small teams | Free plan, marketing integration, user-friendly |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Enterprises using Microsoft stack | Data unification, workflow automation |
| Pipedrive | Sales-focused teams | Deal tracking, visual pipelines |
| Freshsales by Freshworks | SMBs | AI insights, built-in calling, automation |
| Insightly | Service-based firms | CRM + project management hybrid |
Tip: Start with a free CRM trial before scaling up to enterprise-level features.
Common Gaps and Challenges in CRM Adoption
Although CRMs are effective, they are not without risks and gaps that companies have to overcome to achieve their goals:
- Inadequate User Acceptance: If there isn’t adequate training and a culturally accepted buy-in, employees may not be able to use the CRM consistently, thereby reducing its usefulness.
- Quality of Data Issues: Garbage-in, garbage-out. If customer information isn’t complete or outdated, the insights may be compromised.
- Integration Issues: Inability to connect CRM to various business apps (billing ERP, billing Support systems) could lead to silos.
- The Wrong Choice for your Industry or Size: Small businesses might over-invest in a system that has a lot of features not used, and a large company could outgrow a basic CRM.
- A lack of Strategies or Objectives that can be Measured: The implementation of CRM must be aligned with business objectives; otherwise, it’s an unintended “tool that has no purpose”.
- Underestimating the Need for Change Management: Introduce new workflows, systems, and processes that change how employees work. If you don’t plan it correctly, the potential for disruption or resistance could be experienced.
- Focusing Too Much on Features Rather than Results: Some organizations evaluate CRM based on features, rather than on how it contributes to business outcomes. This is the issue that a lot of recent articles discuss.
The article highlights the gaps in implementation in discussions about CRM: while companies focus on features and benefits, they do not focus on the management of change strategies, governance, and the strategy required to achieve successful implementation. A well-written article can bridge this gap by offering instructions regarding how best to use the system, and not just the reason to buy.
How to Select the Best CRM System
When deciding on a CRM, companies should take into account:
- Fit for Size Business and a Model: Is the CRM appropriate for mid-market, SMB, or large-scale enterprises?
- Capabilities Specific to Industry: Does it work with the particular workflows of the business (B2B in contrast to B2C, manufacturing, service-based, etc.)?
- User-friendliness and User Experience: How will staff be able to adopt it quickly? Mobile access and an intuitive interface matter.
- Integration Capability: Does it have the ability to integrate with existing systems (ERP support, marketing, and finance)?
- Flexibility and Scalability: Can it expand along with your business? Can processes be adapted to meet specific needs?
- Analytics and Capabilities for Insights: Can the CRM offer more than information capture, but also valuable insight and planning?
- Support Vendor and Ecosystem: Does the vendor offer support, training, community, and a marketplace for extensions?
- The total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider licensing, implementation, maintenance, training, and upgrades.
- Compliance and Security of Data: Particularly crucial in industries that are regulated or when dealing with sensitive personal information.
- A precise Strategic Alignment: Determine the business outcomes you want to achieve (e.g., growth in revenue, better retention, and lower cost of service) and ensure that your CRM is in line with those goals.
It is the Future of CRM Systems: Trends to Watch
Systems for CRM continue to develop quickly. Here are some of the key trends emerging:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): They allow CRMs to give predictive suggestions (which customers are more likely to buy, and they follow up) and automate tasks such as the entry of data and lead scoring.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDP) Integration: Integrating CRM with more detailed analytics of customer data creates unified profiles that cover social, demographics, and emotions.
- Omnichannel and Remote-first Experience: Including chatbots, mobile, social Voice, and traditional channels, CRMs will continue to need a seamless user experience across channels.
- IOT and Connected Devices: Businesses that use tangible products (e.g., automobiles, appliances, etc.) CRM can incorporate data from device usage for service reminders, referrals, or upselling.
- A greater Focus on the Customer Lifecycle (not only selling): A shift from acquisition-centric to retention-focused CRM models, focusing on the long-term benefits rather than only the initial sale.
- Automated Workflows and Increased Automation: RPA (Robotic Process Automation) integrated into CRM to take care of tasks that are repetitive and allow humans to concentrate on more valuable work.
- Best Mobile and Artificial Intelligence-Driven Experience: Making the CRM available, user-friendly, and valuable to remote deskless, field workers, or those who work from home.
- Privacy Compliance, Ethical and Privacy AI: The rise of ethical AI regulations (GDPR and CCPA), CRMs will have to help with consent management as well as data traceability, and the ethical use of AI.
Final Thoughts
In essence, a CRM system goes beyond the basic contact book. It’s an integrated platform that links sales, marketing operations, as well as service and support to the demands of the customers. If it’s implemented and chosen appropriately, it can become an effective tool for improving efficiency and understanding, as well as growth. However, technology is only one part of a larger picture. The success of adoption depends on the integration of the process, system, and staff.
Since expectations for customers are constantly changing and business environments grow more complex, a modern CRM system is vital. It doesn’t matter if you’re an emerging company just beginning or a global enterprise with many countries; the right CRM software will aid in managing your relationships, enhancing processes, and increasing the value for your clients.
FAQs
1. What is CRM?
CRM is a term used to describe Customer Relationship Management. It refers to both strategies and practices as well as the systems of software employed to manage customer relationships.
2. What is the difference between a CRM system and a Contact Management System?
A contact management system stores simple contact details. CRM systems add interaction history, pipeline monitoring analytics, workflow automation, and analytics for marketing, sales, and service.
3. What CRM types exist?
There are various types of CRM of CRM: Operational (sales and service, as well as marketing tracking), Analytical CRM (data/insights), and collaborative CRM (cross-team coordination). Additionally, by deployment, cloud-based vs. on-premise.
4. Does every company need a CRM?
Absolutely, every business that interacts with potential customers or clients will benefit from the use of a CRM. The requirements and the complexity of a CRM depend on the size, industry, and operations.
5. What are the main challenges in implementing the CRM?
A few common problems: low user engagement, inadequate data, poor connections with different systems, a lack of a clear plan or objective, and underestimating the importance of change management.
6. What is the cost of a CRM system?
Costs vary based on features and the quantity of users, type of deployment (cloud as opposed to on-premise), as well as integrations and the need for customisation. A lot of providers offer tiered pricing and scaling.
7. What features should I search for in the CRM system?
Key features include a unified customer database, workflow automation, analytics dashboards, integration capabilities, mobile access, data security, and scalability/customisation.
8. What’s the next orientation of CRM?
Future CRMs will incorporate AI machines, machine learning, and automation to offer predictions, and converge into larger databases of customer information, facilitate multichannel customer engagement, connect IoT, and emphasize the lifetime value of customers over mere acquisition.
